In the realm of healthcare, understanding hypoglycemia and its intricacies is paramount. As we delve into the topic, we shall dissect a crucial question: “Which statement about hypoglycemia is false?” Embarking on this journey, we will unravel common misconceptions, arming you with accurate knowledge and empowering you to make informed decisions regarding this condition.
Hypoglycemia, a state characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, can manifest in various ways. Its symptoms range from subtle tremors to severe seizures. Understanding the causes, such as diabetes medications or insulin overdose, is essential for effective management. However, certain misconceptions persist, potentially leading to improper treatment or delayed diagnosis.
Definition of Hypoglycemia

Hypoglycemia is a medical condition characterized by abnormally low levels of glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream. It occurs when the body does not have enough glucose to meet its energy demands. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the brain and other vital organs, and its depletion can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Physiologically, hypoglycemia arises from an imbalance between glucose production and utilization. In healthy individuals, the body maintains a relatively constant blood glucose level through a complex interplay of hormones and metabolic processes. When glucose levels drop below normal, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia, Which statement about hypoglycemia is false
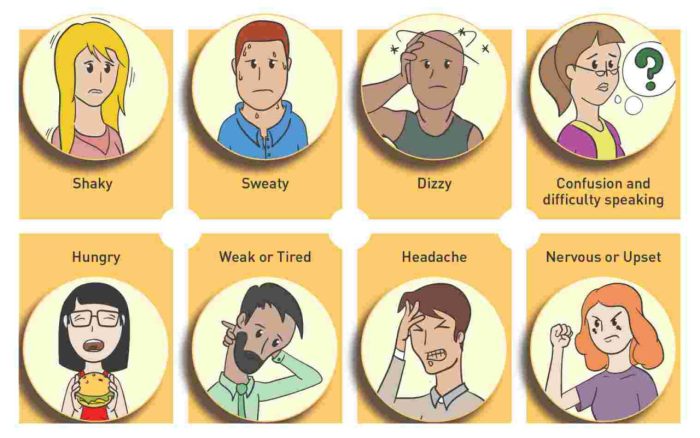
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild hypoglycemia may cause subtle symptoms, such as:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Hunger
- Pale skin
- Dizziness
- Confusion
As hypoglycemia worsens, more severe symptoms may develop, including:
- Anxiety
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
Causes of Hypoglycemia
The most common cause of hypoglycemia is the use of diabetes medications, such as insulin or sulfonylureas. These medications lower blood glucose levels by increasing insulin production or sensitivity, and if taken in excess or in combination with other factors, can lead to hypoglycemia.
Other causes of hypoglycemia include:
- Insulin overdose
- Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease, and adrenal insufficiency
- Alcohol consumption
- Intense physical activity
Treatment of Hypoglycemia
The immediate treatment for suspected hypoglycemia is to consume a source of glucose, such as glucose tablets, candy, or a sugary drink. This will help to raise blood glucose levels quickly and alleviate symptoms.
If the individual is unconscious or unable to swallow, glucagon can be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Glucagon is a hormone that stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream.
Prevention of Hypoglycemia
Preventing hypoglycemia in individuals at risk, such as those with diabetes, is crucial. Strategies include:
- Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly
- Taking diabetes medications as prescribed
- Eating regular meals and snacks
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular exercise
Misconceptions about Hypoglycemia
There are several common misconceptions about hypoglycemia that can be harmful if not corrected. These include:
- Hypoglycemia is only a concern for people with diabetes.While diabetes is the most common cause of hypoglycemia, it can also occur in individuals without diabetes.
- Hypoglycemia is always caused by not eating enough.Hypoglycemia can occur even in individuals who have eaten recently, especially if they are taking diabetes medications or have certain medical conditions.
- Hypoglycemia is not a serious condition.Hypoglycemia can be a serious medical emergency if not treated promptly. It can lead to seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death.
Top FAQs: Which Statement About Hypoglycemia Is False
Is it true that hypoglycemia is always caused by diabetes?
No, while diabetes is a common cause, hypoglycemia can also result from other factors such as insulin overdose, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions.
Can hypoglycemia be prevented?
Yes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular meals, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and managing underlying conditions, can help prevent hypoglycemia.
Is it safe to treat hypoglycemia with sugary drinks?
Yes, sugary drinks can provide a quick source of glucose to raise blood sugar levels. However, it’s important to follow up with a balanced meal to prevent a rebound in blood sugar levels.