CPT code FEM POP Bypass refers to a specific procedure performed to address complex vascular conditions affecting the lower extremities. This in-depth guide delves into the intricacies of this procedure, providing a comprehensive overview of its purpose, indications, and outcomes.
As we explore the intricacies of CPT code FEM POP Bypass, we will delve into the indications for this procedure, including the underlying conditions that may necessitate its implementation. Furthermore, we will examine the meticulous preoperative preparation, the surgical technique itself, and the essential postoperative care required for a successful recovery.
CPT Code FEM POP Bypass
CPT code FEM POP Bypass stands for Femoral-Popliteal Bypass Surgery. It is a surgical procedure used to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD) in the legs.
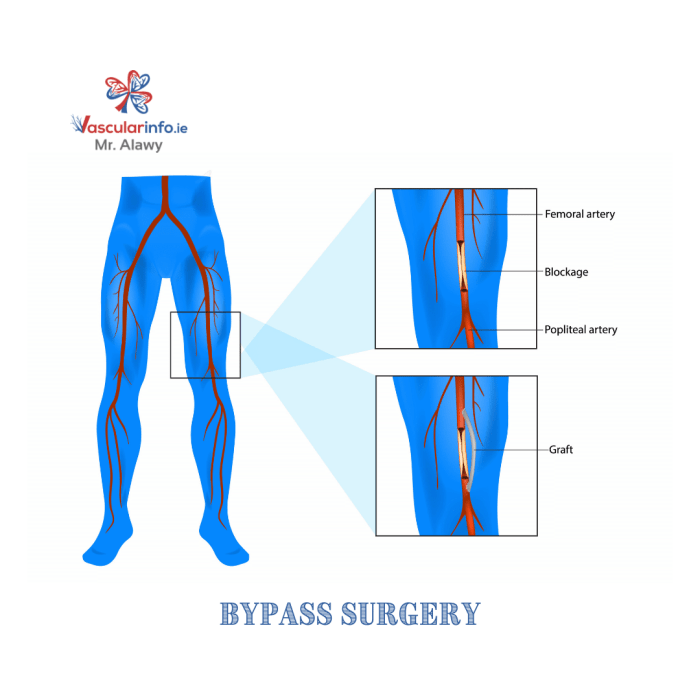
The purpose of the procedure is to create a new pathway for blood to flow around a blocked or narrowed artery in the leg. This is done by grafting a healthy blood vessel, typically taken from the patient’s own body, onto the blocked artery.
Procedure Steps
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- An incision is made in the groin area.
- The blocked artery is identified and a graft is prepared.
- The graft is sewn onto the blocked artery.
- The incision is closed.
Indications for FEM POP Bypass
FEM POP bypass is a surgical procedure indicated to restore blood flow to the lower extremity when other less invasive treatments have failed. The underlying conditions that may necessitate this procedure include:
- Severe peripheral artery disease (PAD):PAD is a condition in which the arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the lower extremities.
- Critical limb ischemia (CLI):CLI is a severe form of PAD that can lead to tissue death and amputation if left untreated.
- Failed endovascular interventions:Endovascular interventions, such as angioplasty and stenting, are less invasive procedures used to open blocked arteries. However, in some cases, these procedures may fail, necessitating a bypass surgery.
Patient Selection Criteria
The selection of patients for FEM POP bypass is based on several factors, including:
- Severity of symptoms:Patients with severe symptoms, such as pain, numbness, or difficulty walking, are more likely to benefit from surgery.
- Extent of disease:The extent of the arterial blockage and the number of arteries affected determine the complexity of the surgery and the likelihood of success.
li> Patient’s overall health:Patients with other medical conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes, may be at higher risk for complications during surgery.
Preoperative Preparation
Prior to undergoing a FEM POP bypass, patients undergo meticulous preparation to optimize their surgical outcomes and recovery.
Patient education and counseling play a crucial role in ensuring the patient’s understanding of the procedure, its potential risks and benefits, and the expected recovery process. The healthcare team provides detailed information about the surgery, anesthesia, and postoperative care, addressing any questions or concerns the patient may have.
When it comes to cpt code fem pop bypass, understanding the veins of the body is crucial. To enhance your knowledge, check out this comprehensive veins of the body quiz . It provides an interactive way to test your grasp of venous anatomy, which is essential for successful cpt code fem pop bypass procedures.
Preoperative Imaging and Laboratory Tests
To assess the patient’s overall health and prepare for the surgery, several imaging and laboratory tests are performed.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Echocardiogram:These tests evaluate the heart’s electrical and structural integrity, ensuring that it can withstand the demands of surgery.
- Chest X-ray:This provides a view of the lungs and heart, assessing for any underlying respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
- Blood Tests:Complete blood count, coagulation profile, and chemistry panel are performed to assess the patient’s blood composition, clotting ability, and overall organ function.
- Imaging Studies:Depending on the patient’s specific condition, imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to visualize the pelvic anatomy and assess the extent of the prolapse.
Surgical Technique
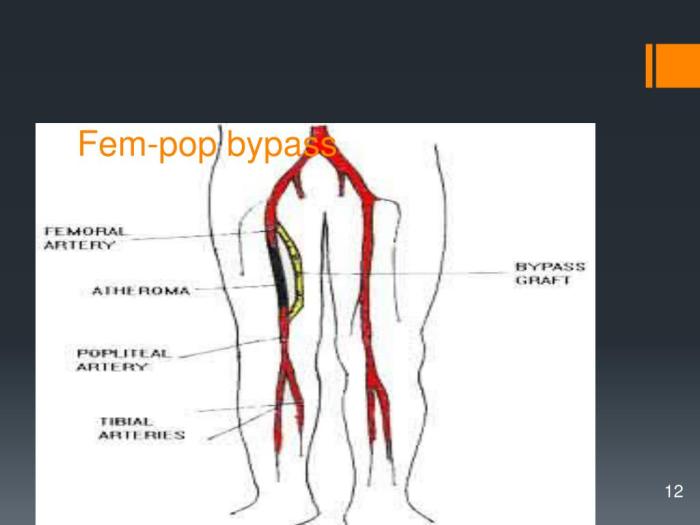
The surgical technique for FEM POP Bypass involves creating a bypass graft between the femoral artery and the popliteal artery to restore blood flow to the lower leg. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia.
Incision and Exposure
A longitudinal incision is made along the medial aspect of the thigh, extending from the inguinal crease to the popliteal fossa. The superficial fascia is incised, and the saphenous vein is ligated and divided. The profunda femoris artery and vein are identified and mobilized.
The femoral artery and vein are then exposed.
Graft Preparation
A suitable graft is selected, typically a vein graft from the ipsilateral great saphenous vein or a prosthetic graft. The graft is prepared by trimming and tailoring it to the appropriate length and diameter.
Anastomosis
The graft is anastomosed end-to-side to the femoral artery and end-to-side to the popliteal artery. The anastomoses are typically performed using a running suture technique.
Closure, Cpt code fem pop bypass
Once the anastomoses are complete, the graft is covered with surrounding tissue and the incision is closed in layers. The superficial fascia is closed with a running suture, and the skin is closed with a subcuticular suture.
Potential Complications
The potential complications associated with FEM POP Bypass include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Graft occlusion
- Limb ischemia
- Neurological injury
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for FEM POP bypass involves managing pain, ensuring proper wound healing, and initiating rehabilitation to restore function and mobility.
Pain management typically involves administering pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications to minimize discomfort. The wound is closely monitored for signs of infection or complications, and dressings are changed regularly to promote healing.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation after FEM POP bypass aims to gradually restore mobility and function to the affected leg. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in this process, focusing on exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and balance.
- Early mobilization is encouraged, with patients advised to start walking as soon as possible after surgery.
- Exercises are gradually progressed to increase flexibility, muscle strength, and coordination.
- Patients are educated on proper posture and body mechanics to prevent further injury.
Recovery time varies depending on the individual’s overall health and the severity of the procedure. Most patients can expect to resume normal activities within 6-8 weeks after surgery, but full recovery may take several months.
Outcomes and Prognosis
Femoropopliteal (FEM-POP) bypass surgery generally yields favorable outcomes, with high success rates and significant improvement in symptoms.
The success of FEM-POP bypass is primarily assessed by the restoration of blood flow to the affected limb and the resolution of symptoms, such as pain, claudication, and tissue loss. Success rates vary depending on factors like the severity of the underlying condition, patient’s overall health, and the skill of the surgeon.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Monitoring
Long-term follow-up is crucial to monitor the durability of the bypass graft and the overall health of the patient. Regular check-ups typically include physical examinations, imaging tests (such as duplex ultrasound or angiography), and assessment of symptoms.
The monitoring plan aims to detect any signs of graft failure or recurrence of symptoms early on, allowing for prompt intervention and management.
Alternatives to FEM POP Bypass
When considering FEM POP Bypass, it’s crucial to explore alternative treatments that address the underlying conditions necessitating the bypass. These alternatives offer varying advantages and disadvantages, and a thorough evaluation is essential to determine the most suitable option for each individual.
Medical Management
- Medications:Antihypertensives, lipid-lowering drugs, and antiplatelet agents can help manage underlying cardiovascular risk factors and prevent further plaque buildup.
- Lifestyle Modifications:Diet, exercise, and smoking cessation can improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of future blockages.
Endovascular Interventions
- Balloon Angioplasty:A catheter with a balloon tip is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to widen the lumen.
- Stenting:A small mesh tube (stent) is placed in the artery to keep it open and prevent re-narrowing.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| FEM POP Bypass | – Durable, long-term solution
|
– Invasive surgery
|
| Medical Management | – Non-invasive
|
– May not be effective for severe blockages
|
| Endovascular Interventions | – Less invasive than surgery
|
– May not be suitable for all blockages
|
Common Queries: Cpt Code Fem Pop Bypass
What is the purpose of CPT code FEM POP Bypass?
CPT code FEM POP Bypass is used to describe a surgical procedure that creates a new pathway for blood flow in the lower extremities, bypassing blockages or narrowing in the arteries.
What are the indications for CPT code FEM POP Bypass?
Indications for CPT code FEM POP Bypass include severe peripheral artery disease, critical limb ischemia, and chronic wounds that have failed to respond to other treatments.
What are the potential complications of CPT code FEM POP Bypass?
Potential complications of CPT code FEM POP Bypass include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and nerve damage.